Condition:New
Type:Logic ICs
Product description
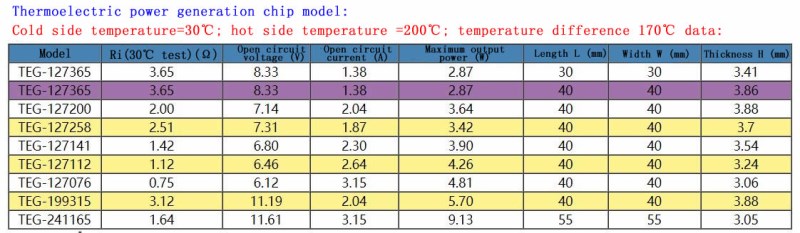
The thermoelectric power sheet is assembled from high-strength bismuth telluride thermoelectric material, high thermal conductivity and high insulation DBC (Direct Bonded Copper) ceramics and high temperature solder. It is suitable for use in an environment where the hot end is 200°C.
Product Features
●High performance, the power generation efficiency can reach 5% under a temperature difference of 200 degrees
●High reliability, more than 10 years of normal application life
●High temperature resistance, hot surface can be used at 200℃
●High fine flatness (±0.02mm)
●Meet RoSH requirements and provide customized services
Application field
▲Fireplace fan
▲Outdoor barbecue grill
▲Power supply for low power consumption electronic equipment
▲Fire Control System
▲Control System
Application note
·The power generation module must be installed on a flat surface, and the flatness of the contact surface is required to be above 30 microns;
·The pressing force must be no less than 12-15KG/CM2
·The hot surface temperature cannot exceed 200 degrees.

Installation note
■ Use direct current (DC) power supply; voltage/current should be less than the maximum voltage/current of the device;
■ The cooling fins should be installed on the hot-end radiator before use, generally using fans and radiators or water cooling;
■ Use and store in an environment less than 100°C;
■ Pay attention to the force balance during installation to prevent side pressure or any form of impact;
■ This product is suitable for temperature cycles from 0 to 60°C. If it is applied to a wide range of temperature cycles, corresponding life tests are required;
Quick product selection
1. Determine whether the refrigeration object (space, liquid, solid) has a heat source and what is the heating power;
2. What is the ambient temperature (°C) used and the target temperature (°C) of the refrigerating object; Item 1 and Item 2 quickly determine whether it is appropriate to use semiconductor refrigeration chips.
3. Determine the maximum product size that the product can be applied to. From the perspective of performance, the larger the size, the better the cooling effect;
4. If high cooling power is required, you can consider using multiple pieces in series and parallel;
5. If the input voltage exceeds 12V, it is recommended to consider using a multi-chip series solution;
6. The better the heat dissipation effect, the better the cooling effect;
7. The greater the temperature difference, the lower the cooling efficiency;
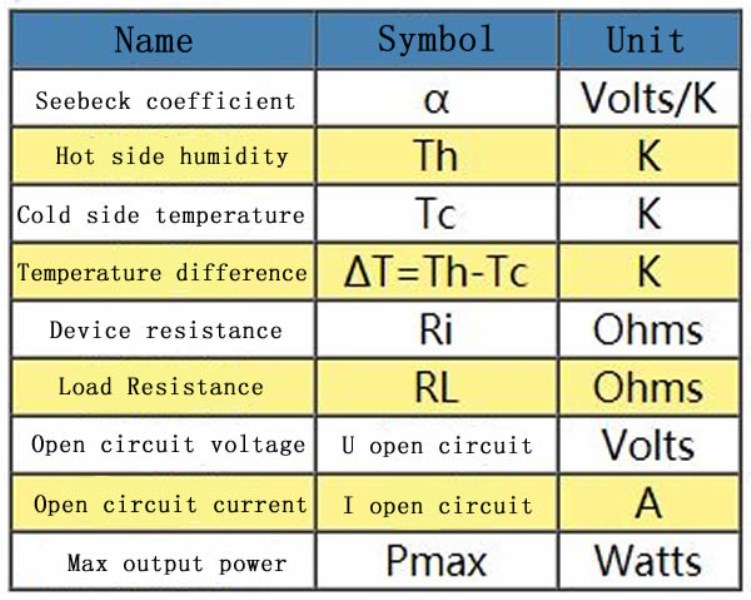
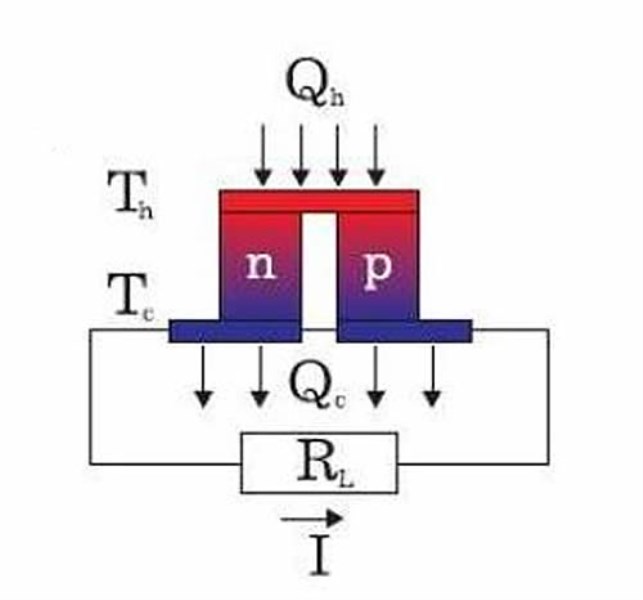
The four main performance parameters of the semiconductor refrigerator are:
Maximum current Imax: Refers to the maximum current value when ΔT reaches ΔTmax when ΔT reaches ΔTmax under the condition of constant hot surface temperature Th and load Qc.
Maximum current Umax: refers to the constant hot surface temperature Th, the load Qc is 0, the voltage value when ΔT reaches ΔTmax is the maximum voltage value.
Maximum temperature difference ΔTmax: When the heat absorption of the cold surface is 0, the temperature of the hot surface is constant. When I=Imax, the maximum temperature difference between the cold surface and the hot surface can be reached.
Maximum heat absorption QCmax: constant hot surface temperature, the temperature difference between the cold surface and the hot surface ΔT=0, when I=Imax, the cooling surface can absorb the heat.
Process test items
● Thermoelectric material resistance, thermal resistance, Seebeck coefficient test
● Chip height tolerance
● Metallization layer adhesion test
● Solderability test of metallization layer
● Die PN pole test
● Ceramic chip crack test
● Solder joint welding quality test
● Measurement of the maximum temperature difference, resistance, and maximum cooling capacity of the device
Reliability test standards
● A cold technology refrigeration sheet is tested according to the following standards:
● American military standard: MIL-SDT-883E
● Communication industry standard: Telcordia GR-468
● Test standard for temperature circulator
Reliability test items
● Temperature Cycling
● Thermal Shock Testing
● High Temperature Storage
● Power On/Off Cycling Test
● Reverse Power Cycling Test (Reverse Power Cycling Test)
● Mechanical Shock Testing
● Variable Frequency Vibration Testing

